Ziehl-Neelsen Staining- Principle and Procedure with Results

Objectives of the Ziehl-Neelsen Staining
- To differentiate between acid-fast bacilli and non-acid-fast bacilli.
- To stain Mycobacterium species.
Principle of the Ziehl-Neelsen Staining
- The Ziehl-Neelsen stain uses basic fuchsin and phenol compounds to stain the cell wall of Mycobacterium species.
- Mycobacterium does not bind readily to simple stains and therefore the use of heat along with carbol-fuschin and phenol allows penetration through the bacterial cell wall for visualization.
- Mycobacterium cell wall contains high lipid content made up of mycolic acid on its cell wall making it waxy, hydrophobic, and impermeable. These are ß -hydroxycarboxylic acids made up of 90 carbon atoms that define the acid-fastness of the bacteria.
- Use of Carbol-fuschin which is basic strongly binds to the negative components of the bacteria which include the mycolic acid and the lipid cell wall. addition of acid alcohol along with the application of heat forms a strong complex that can not be easily washed off with solvents.
- The acid-fast bacilli take up the red color of the primary dye, carbol-fuschin.
- While non-acid-fast bacteria easily decolorize on the addition of the acid-alcohol and take up the counterstain dye of methylene blue and appear blue
- This technique has been used in the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae.
Reagents used in the Ziehl-Neelsen Stain
- Carbol-Fuschin (Primary dye)
- 20% sulphuric acid or acid-alcohol (Decolorizer)
- Methylene Blue dye (counterstain) or malachite green
Preparation of reagents
Carbol fuschin
- Distilled water- 100ml
- Basic fuschin- 1g
- Ethyl alcohol (100% ethanol)- 10ml
- Phenol crystals- 5ml
Acid alcohol (3% hydrochloric acid in 95% ethyl alcohol)
- Ethyl alcohol- 95 ml
- Distilled water- 2 ml
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid- 3 ml
0.25% methylene blue in 1% acetic acid
- Methylene blue- 0.25g
- Distilled water- 99ml
- Acetic acid- 1ml
Procedure for Ziehl-Neelsen Staining
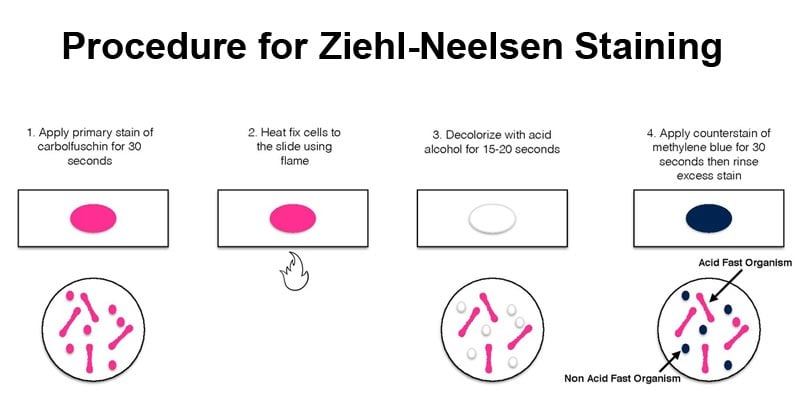
- On a clean sterile microscopic slide, make the smear of the sample culture and heat fix the smear over blue heat.
- Over the smear, pour and flood the smear with carbol fuschin and heat gently until it produces fumes.
- Allow it to stand for 5 minutes and wash it off with gently flowing tap water.
- Add 20% sulphuric acid and leave it for 1-2 minutes. Repeat this step until the smear appears pink in color.
- Wash off the acid with water.
- Flood the smear with methylene blue dye and leave it for 2-3 minutes and wash with water.
- Air dry and examine the stain under the oil immersion lens.
Results and Interpretation

Figure: Mycobacterium tuberculosis visualization using the Ziehl–Neelsen stain. Image Source: CDC/Dr. George P. Kubica.
- Acid-fast bacteria retain the primary dye, carbol-fuschin, and stain pink.
- Non-acid fat bacteria take up the methylene blue dye and appear blue.
Applications of Ziehl-Neelsen Staining
- Used for examination and identification of Mycobacterium species.
- Used to differentiate between acid-fast and non-acid fast bacilli
- Used for the identification of some fungal species such as Cryptosporidium.
Limitations of Ziehl-Neelsen Staining
- It can only be used to identify acid-fast bacilli.
- The physical morphology of the organism is distorted.
References and Sources
- 2% – https://labhelpline.com/2019/05/23/ziehl-neelsen-staining-technique-for-acid-fast-bacilli/
- 1% – https://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/units/acidfast_stain.html
- 1% – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17533853/
- 1% – https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-acid-fast-and-vs-non-acid-fast-bacteria/
- 1% – https://www.carolina.com/specialty-chemicals-a/acid-alcohol-3-hydrochloric-acid-in-95-ethanol-laboratory-grade-500-ml/841733.pr
- 1% – http://whocctblab.fondazionesanraffaele.it/uploads/2/0/8/2/20828554/_ios_ebp-ziehl-neelsen_staining.pdf
-
-
-
-
About Author




